Manufacturing Process of Solar Panels: A Comprehensive Guide

Solar panel manufacturing is the backbone of solar energy generation. Every solar panel you see on a rooftop or solar plant goes through a detailed, carefully controlled process to ensure it produces clean, reliable power for 25 years or more. I This article is written to genuinely help you understand the topic-whether you’re a student, business owner, EPC contractor, or someone planning to invest in solar energy with KLK India. Why Understanding the Solar Panel Manufacturing Process Matters Before buying or installing a solar panel, most people focus only on price and wattage. But the manufacturing process of solar panels directly impacts: Power output and efficiency Durability in Indian weather conditions Long-term performance and degradation rate Safety and reliability When you understand how a solar panel is made, you can make smarter decisions, avoid low-quality products, and get better returns from solar energy. What Is a Solar Panel Made Of? A solar panel is not a single sheet of glass. It’s a combination of multiple layers, each with a specific role in converting sunlight into electricity. Main Components of a Solar Panel Silicon solar cells – Convert sunlight into electricity Tempered glass – Protects cells from weather EVA (Ethylene Vinyl Acetate) sheets – Encapsulate and cushion cells Backsheet – Provides insulation and protection Aluminium frame – Gives strength and mounting support Junction box – Transfers generated power to external cables Each component goes through its own preparation stage before final assembly. Types of Solar Panels Based on Manufacturing Before diving into the manufacturing steps, it’s important to know the types of solar panels, because the process slightly varies. 1. Monocrystalline Solar Panels Made from a single crystal of silicon Higher efficiency Longer lifespan Slightly higher cost 2. Polycrystalline Solar Panels Made from multiple silicon crystals Lower efficiency than mono More affordable Widely used in large solar projects 3. Thin-Film Solar Panels Made by depositing thin layers of photovoltaic material Lightweight and flexible Lower efficiency Used in specific applications Most manufacturers, including KLK India, focus mainly on monocrystalline and polycrystalline solar panels because they offer the best balance of performance and cost. Raw Materials Used in Solar Panel Manufacturing The quality of raw materials plays a major role in solar panel performance. Key Raw Materials High-purity silicon Silver paste (for electrodes) Aluminium (for frames) Copper (for wiring) Glass (low-iron tempered glass) High-grade raw materials ensure better efficiency and lower degradation over time. Step-by-Step Manufacturing Process of Solar Panels Now let’s understand the solar panel manufacturing process step by step, from raw silicon to a finished panel ready for installation. Step 1: Silicon Purification Silicon is the heart of every solar panel. However, natural silicon contains impurities and must be purified. How It Works Silicon is extracted from sand (silica) It is heated in a furnace at very high temperatures Impurities are removed to get 99.99% pure silicon This purified silicon is called solar-grade silicon. Why it matters: Higher purity silicon = better solar energy conversion. Step 2: Silicon Ingot Formation Purified silicon is melted and formed into solid blocks called ingots. Two Methods Monocrystalline ingots – Grown as a single crystal Polycrystalline ingots – Formed by cooling silicon in molds These ingots determine whether the final solar panel will be mono or poly type. Step 3: Wafer Slicing Silicon ingots are sliced into ultra-thin sheets called wafers. Key Points Thickness is around 160–180 microns Diamond wire saws are used for precision Wafers are cleaned to remove dust and damage Even a small crack in a wafer can affect the entire solar panel. Step 4: Doping the Silicon Wafers Doping is the process of adding small amounts of other elements to silicon. Purpose of Doping Improves electrical conductivity Creates positive (P-type) and negative (N-type) layers Common doping elements: Boron Phosphorus This step enables the wafer to generate electric current when sunlight hits it. Step 5: Anti-Reflective Coating Bare silicon reflects sunlight, which reduces efficiency. Solution A thin anti-reflective coating (usually silicon nitride) is applied Reduces reflection Helps absorb more solar energy That’s why solar cells appear dark blue or black. Step 6: Solar Cell Formation Now the wafer officially becomes a solar cell. What Happens Here Metal contacts (front and back) are added using silver and aluminium paste These contacts collect and transfer electricity Cells are tested for voltage and efficiency Cells that don’t meet quality standards are rejected at this stage. Step 7: Sorting and Grading of Solar Cells Not all solar cells perform equally. Cells Are Sorted Based On Efficiency (%) Power output Voltage consistency Only cells with similar ratings are grouped together. This ensures uniform performance in the final solar panel. Step 8: Module Assembly (Cell Stringing) Now multiple solar cells are connected together. Process Cells are soldered in series and parallel Form strings that match the panel’s wattage Precision machines ensure proper alignment Even small misalignment can reduce panel efficiency. Step 9: Lamination Process This is one of the most critical stages in solar panel manufacturing. Layer Structure (Top to Bottom) Tempered glass EVA sheet Solar cells EVA sheet Backsheet These layers are sealed together in a laminator under heat and vacuum. Result: A weatherproof, long-lasting solar panel structure. Step 10: Framing and Junction Box Installation Aluminium Frame Adds mechanical strength Helps with mounting Junction Box Fixed at the back of the panel Contains bypass diodes Ensures safe power transfer This step makes the solar panel ready for real-world installation. Step 11: Testing and Quality Checks Every solar panel must pass strict quality tests. Common Tests Flash test (measures power output) Insulation test Mechanical load test Hot spot test EL (Electroluminescence) test Only panels that meet international standards are approved for dispatch. Simple Table: Solar Panel Manufacturing Stages Stage Process Name Purpose 1 Silicon Purification Remove impurities 2 Ingot Formation Create silicon blocks 3 Wafer Cutting Make thin silicon wafers 4 Doping Improve conductivity 5 Anti-Reflective Coating Reduce light reflection 6 Cell Formation Generate electricity 7 Cell Sorting Ensure uniform performance 8 Module Assembly Connect cells 9
Solar Rooftop vs Solar Panels – Which Solar Energy Option Is Best?

Renewable energy is no longer a future idea-it’s a real, practical solution, and solar energy is leading the way. When people think about switching to solar panels or a solar rooftop, the first question is usually simple: Which one is right for me? The answer depends on your roof, budget, power needs, and long-term plans-not just trends. This guide breaks everything down in clear, simple language so you can make a smart, confident decision without confusion or sales pressure. Introduction: Understanding Solar Energy Options As the world moves towards renewable energy, solar energy has become one of the easiest and most reliable ways to generate electricity. In India especially, with high sunlight availability, both solar rooftop systems and solar panels are popular choices for homes, businesses, schools, and factories. While people often use the terms interchangeably, solar rooftop and solar panels are not exactly the same thing. They serve the same goal—producing clean electricity—but they work differently and suit different needs. If you’re planning to invest in solar energy, understanding this difference can save you money, time, and future regret. What Is a Solar Rooftop System? A solar rooftop system is a complete setup installed on the roof of a building to generate electricity using sunlight. It usually includes: Solar panels Mounting structure Inverter Wiring and safety equipment The term solar rooftop refers to the entire system, not just the panels. It means your roof is being used as a power-generating space. There are two common types of solar rooftop systems: Grid-connected (On-grid) Off-grid or Hybrid (with battery backup) Most urban homes and commercial buildings choose grid-connected solar rooftops because they are cost-effective and easy to maintain. What Are Solar Panels? Solar panels are the main components of any solar energy system. They are made of photovoltaic (PV) cells that convert sunlight into electricity. When sunlight hits the panel: PV cells absorb sunlight Electrons start moving Electricity is generated in DC form The inverter converts it into AC electricity for daily use Solar panels can be installed: On rooftops On ground-mounted structures On sheds, parking areas, or open land In short, solar panels are the tools, and the solar rooftop is the system that uses them. Solar Rooftop vs Solar Panels: Core Difference Many people ask: Solar rooftop vs solar panels—what’s the real difference? Here’s the simplest way to understand it: Solar panels are individual units that generate electricity Solar rooftop is a complete power system using solar panels installed on your roof To make it clearer, here’s a simple comparison table. Solar Rooftop vs Solar Panels: Comparison Table Feature Solar Rooftop System Solar Panels Meaning Complete solar power setup on roof Individual power-generating units Includes Panels, inverter, wiring, structure Only panels Usage Direct electricity for home/business Needs system to function Installation Planned as a full project Installed as part of system Best for Long-term power savings Flexible energy setups Maintenance Low, system-based Depends on setup Scalability Limited by roof size Easy to add more panels How a Solar Rooftop System Works A solar rooftop system works quietly in the background once installed: Solar panels absorb sunlight during the day Electricity flows to the inverter Inverter converts power for appliances Extra electricity goes to the grid (in on-grid systems) You use solar power first, grid power only when needed This reduces electricity bills and dependence on conventional power. Benefits of Solar Rooftop Systems 1. Lower Electricity Bills Solar rooftops significantly reduce monthly power costs. In many homes, bills drop by 60–90%. 2. Better Use of Empty Roof Space Your roof becomes a productive asset instead of just a shelter. 3. Supports Renewable Energy Goals Using solar energy reduces carbon emissions and fossil fuel use. 4. Long-Term Investment Most systems last 25 years or more with minimal maintenance. 5. Net Metering Advantage In many regions, excess power sent to the grid earns credits. Benefits of Solar Panels 1. Proven Technology Solar panels have been used globally for decades and are reliable. 2. Flexible Installation They can be installed on different surfaces—not just rooftops. 3. Easy to Upgrade You can add more panels later as energy needs grow. 4. Cost Control You can start small and expand gradually. Which Option Is Better for Homes? For most residential users, a solar rooftop system is the better choice because: It’s designed for daily household consumption Works smoothly with the electricity grid Requires little involvement after installation However, if you have limited roof space or plan future expansion, focusing on high-efficiency solar panels within a rooftop system is important. Which Option Is Better for Businesses? Commercial users usually focus on: Power output Return on investment System scalability In this case: Solar rooftop systems work best for offices, schools, hospitals Solar panels with ground mounting suit factories or warehouses Cost Comparison: Solar Rooftop vs Solar Panels Below is a basic standard cost range to help you understand pricing. Actual prices may vary depending on location, brand, and installation conditions. System Size Approximate Cost (₹) 1 kW ₹50,000 – ₹70,000 3 kW ₹1.5 – ₹2.1 lakh 5 kW ₹2.5 – ₹3.5 lakh 10 kW ₹5 – ₹7 lakh Important Factors to Consider Before Choosing 1. Roof Size and Strength Older roofs may need reinforcement. 2. Sunlight Availability Shadows from trees or nearby buildings affect performance. 3. Daily Power Consumption Higher usage needs larger systems. 4. Budget Planning Initial investment vs long-term savings. 5. Local Policies Net metering and subsidies vary by state. Maintenance and Lifespan Solar panels last 25–30 years Inverters last 8–12 years Cleaning panels 2–4 times a year improves output Maintenance is simple and affordable. Environmental Impact By switching to solar energy: You reduce carbon footprint You support renewable energy adoption You reduce dependence on coal-based electricity A typical 5 kW solar rooftop can offset several tons of CO₂ over its lifetime. Solar Rooftop vs Solar Panels: Quick Decision Guide Choose Solar Rooftop if: You want complete power savings You have enough roof space You prefer a long-term solution Choose Solar Panels (flexible setup)
Can Solar Panels Run AC in India? Cost, Setup & Complete Guide
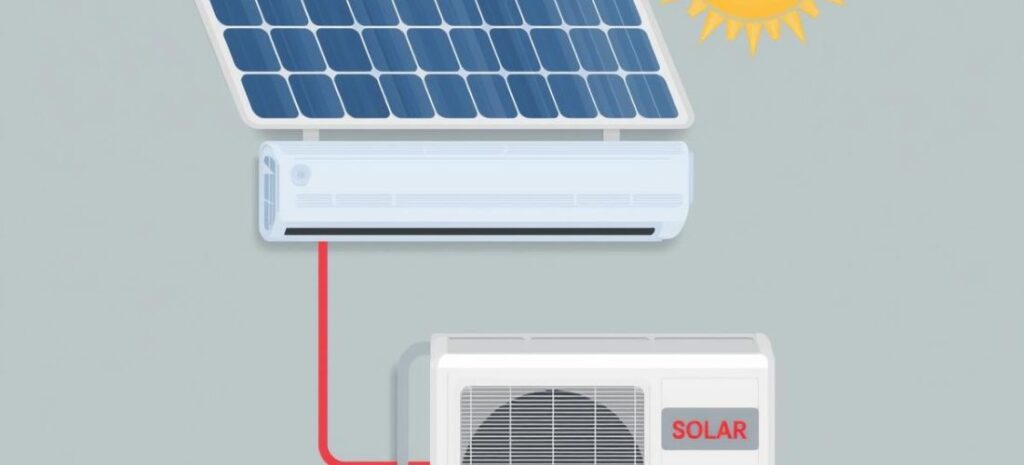
Solar panels are no longer just for lighting homes or running fans. With rising electricity bills and extreme summers, many Indian households are now asking a practical question: Can solar energy run an air conditioner? The short answer is yes, solar panels can run AC in India if the system is designed correctly. India receives abundant sunlight for most of the year, which makes solar energy a strong and reliable option for powering heavy appliances like air conditioners. In this guide, we’ll explain everything clearly-how it works, how much it costs, how many panels you need, and whether it’s worth it for your home. Why More Indians Want to Run AC on Solar Energy Indian summers are getting hotter every year. In many cities, ACs now run for 8-10 hours daily. This leads to: Very high electricity bills Heavy load on the power grid Frequent power cuts in peak summer Increased carbon footprint Solar energy offers a practical solution. Once installed, solar panels generate electricity from sunlight, reducing your dependence on the grid and cutting monthly bills. From my experience working with residential solar projects, most homeowners don’t want to go fully “off-grid.” Instead, they want solar panels to handle AC load during the day and reduce night-time consumption. This is both practical and cost-effective. Can Solar Panels Really Run an Air Conditioner? Yes, solar panels can run an AC, but not directly in most homes. An air conditioner needs: High starting power (surge load) Continuous running power Stable voltage A proper solar AC system uses: Solar panels An inverter (usually hybrid) Batteries (optional but recommended) Grid connection (in most cases) When designed correctly, solar energy can run your AC smoothly without damaging the appliance. Understanding AC Power Consumption in Simple Terms Before choosing solar panels, you must understand how much power your AC consumes. AC Power Demand Basics Startup Power: High power needed when AC compressor starts Running Power: Power used once AC is running normally Daily Units (kWh): Total electricity used per day Common AC Types & Power Consumption AC Type Startup Surge (Watts) Running Power (Watts) Daily Usage (8 Hours) Window AC (1 Ton) 2,000 – 2,500 W 900 – 1,200 W 7 – 9 units Split AC (1.5 Ton) 2,800 – 3,500 W 1,400 – 1,800 W 10 – 14 units Inverter AC (1.5 Ton) 2,000 – 2,500 W 1,000 – 1,300 W 8 – 10 units Central AC (3 Ton) 7,000 – 8,000 W 3,000 – 3,500 W 25 – 30 units Inverter ACs are best for solar energy because they consume less power and handle fluctuations better. How Solar Energy Matches AC Power Needs Solar panels generate electricity only during daylight hours. That’s why system design matters. Key Rule (Industry Standard) To run an AC reliably: Solar system size should be 125%-150% of AC running load This covers power losses, heat, and inverter efficiency For example: 1.5-ton AC (1.5 kW running load) Required solar panel capacity: 2 kW – 2.5 kW How Many Solar Panels Are Needed to Run an AC? There is no fixed number. It depends on: AC size Usage hours Location (sunlight availability) Panel wattage Simple Calculation Method Check AC running watts Multiply by usage hours Divide by average sun hours (India: 4–5 hours) Typical Solar Panel Requirements AC Type Solar Capacity Needed No. of Panels (400W) 1 Ton AC 1.5 – 2 kW 4 – 5 panels 1.5 Ton AC 2 – 3 kW 5 – 7 panels 2 Ton AC 3 – 4 kW 8 – 10 panels 3 Ton AC 6 – 8 kW 15 – 20 panels Rule of Thumb: For every 1 ton of AC, plan 1–1.2 kW of solar panels. Key Components Required to Run AC on Solar Panels 1. Solar Panels Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity. Best choice for AC systems: Monocrystalline panels 400W or higher Efficiency above 20% These panels generate more power in less space, which is important for rooftops. 2. Solar Inverter The inverter converts DC power from solar panels into AC power for your air conditioner. Recommended inverter type: Hybrid inverter (solar + grid + battery) High surge capacity (2x AC startup load) From real installations, I’ve seen AC failures mostly caused by low-quality or undersized inverters. Never compromise here. 3. Battery Batteries store excess solar energy for: Night use Cloudy days Power cuts If you want AC at night, batteries are necessary. Preferred battery type: Lithium-ion (longer life, faster charging) Minimum 5–10 kWh per AC 4. Net Metering (Grid Support) With net metering: Extra solar energy is exported to the grid You get credit units AC can run on grid at night This reduces battery cost and improves ROI. Cost of Running an AC on Solar Panels in India Cost depends on: System size Battery choice Panel brand Installation quality Estimated Cost Table (India) System Type Approximate Cost Payback Period 1.5 Ton AC (2.5 kW solar, no battery) ₹1.5 – ₹2.2 lakh 4–6 years 1.5 Ton AC (2.5 kW + battery) ₹3 – ₹4.5 lakh 6–8 years 3 Ton AC (8 kW hybrid system) ₹7 – ₹10 lakh 7–10 years Grid-tied solar (AC + home load) ₹2 – ₹5 lakh 4–6 years Government Subsidy & Benefits The Indian government supports rooftop solar through: Central Financial Assistance (CFA) State-level subsidies Net metering policies Subsidies mainly apply to grid-connected systems, not battery setups. This can reduce upfront cost by 20–30% in many states. Installation Tips South-facing roof gives best output Tilt angle: 15°–30° Avoid shade at all costs Use proper earthing and surge protection Install AC soft-starter for compressor safety A poorly installed system performs 20–25% worse, even with good panels. Is Your Home Suitable for Solar AC? Ideal Conditions Minimum 100–150 sq. ft. roof space per AC 4+ hours of sunlight daily High electricity bill Inverter or split AC Challenging Conditions Shaded roofs Old wiring Limited terrace space In such cases, high-efficiency panels or partial solar support works better. Advantages of Running AC on Solar Energy Huge electricity
How Much Energy Does a Solar Panel Produce?

A solar panel converts sunlight into usable electricity, also known as solar energy, for homes and businesses. In simple terms, the amount of energy a solar panel produces depends on its size, efficiency, location, and how much sunlight it receives each day. Understanding this clearly helps you decide how many panels you need and whether solar power is worth the investment for you. What Does “Energy Produced by a Solar Panel” Really Mean? Before jumping into numbers, it’s important to understand one basic idea. Power (Watts) = how strong the solar panel is at a given moment Energy (Kilowatt-hours or kWh) = how much electricity the panel produces over time Think of it like water: Power is how fast water flows from a tap Energy is how much water you collect in a bucket over a day, month, or year When people ask, “How much energy does a solar panel produce?” they usually mean how many units (kWh) it generates over time. Average Energy Production of a Solar Panel A modern residential solar panel typically has a power rating of 350W to 450W, with 400W panels being the most common today. Average Energy Output of One Solar Panel Time Period Energy Produced (Approx.) 1 Day 1.5 – 2.5 kWh 1 Week 10 – 17 kWh 1 Month 45 – 75 kWh 1 Year 550 – 900 kWh On average, one solar panel produces about 2 kWh of electricity per day under normal conditions. That may not sound like much, but when you install multiple panels together, the numbers add up quickly. How Many Solar Panels Does a Home Usually Need? Most homes do not rely on just one solar panel. A typical household system includes 15 to 20 solar panels. Example: Average Home Solar System System Size Panels (400W each) Monthly Energy 3 kW 7–8 panels 350–450 kWh 5 kW 12–13 panels 600–750 kWh 6 kW 15 panels 750–900 kWh 10 kW 25 panels 1,200–1,500 kWh A 6 kW solar system is very common and can generate around 900 kWh per month, which is enough for many Indian and global households. What Is the Power Output of a Solar Panel? Power output is measured in watts (W) and tells you the maximum electricity a solar panel can produce under ideal conditions. Popular Solar Panel Power Ratings Brand Model Series Output Range Qcells Q.PEAK DUO 400–405 W JA Solar Deep Blue 3.0 390–400 W Canadian Solar HiKu6 All-Black 395–400 W REC Solar Alpha Pure 400–410 W Silfab Solar Silfab Prime 400–410 W These ratings are tested in labs using Standard Test Conditions (STC): Perfect sunlight Temperature of 25°C No dust, shade, or losses Real-world conditions are different, so actual solar energy production is usually 10-20% lower than lab ratings. Factors That Affect How Much Energy a Solar Panel Produces Several real-world factors decide how much solar energy you actually get. 1. Amount of Sunlight (Peak Sun Hours) The most important factor is how much sunlight your location receives. Peak sun hours mean the number of hours per day when sunlight is strong enough to produce full power. Location Type Peak Sun Hours / Day Very sunny areas 6 – 7.5 hours Moderate sunlight 4 – 5.5 hours Cloudy regions 3 – 4 hours A 400W solar panel: In a sunny area → ~2.8 kWh/day In a cloudy area → ~1.2 kWh/day Even on cloudy days, solar panels still produce electricity-just less. 2. Solar Panel Characteristics Not all solar panels are the same. Panel Type Monocrystalline – Highest efficiency, most popular Polycrystalline – Slightly less efficient, lower cost Thin-film – Lightweight, but lower energy output Most modern homes use monocrystalline solar panels because they produce more solar energy in less space. Panel Efficiency Older panels: 15-18% Modern panels: 20-24% Higher efficiency = more electricity from the same sunlight. 3. Roof Direction and Angle Your roof plays a big role in solar panel performance. Best Roof Direction South-facing roofs produce the most energy East or West-facing roofs work well too North-facing roofs produce the least energy Panel Direction Daily Energy (400W Panel) South 2.0 kWh East 1.7 kWh West 1.7 kWh North 1.4 kWh (Assumes 5 peak sun hours) Roof tilt, shading from trees, dust, and nearby buildings also affect solar energy production. 4. Age of the Solar Panel Solar panels slowly lose efficiency over time. This is called degradation. Average degradation rate: 0.5% per year After 25 years: panel works at ~85% capacity This is normal and already included in most solar system designs. How to Calculate How Much Energy a Solar Panel Produces You can estimate solar energy production using a simple formula: Solar Panel Energy (Wh) = Panel Wattage × Peak Sun Hours Step-by-Step Example Panel size: 400W Sunlight: 5 peak sun hours 400 × 5 = 2,000 Wh per day Convert to kWh: 2,000 ÷ 1,000 = 2 kWh per day Monthly and Yearly Output Daily: 2 kWh Monthly: 2 × 30 = 60 kWh Yearly: 2 × 365 = 730 kWh Multiply this by the number of panels to get your total system output. Power vs Energy: Simple Difference Term Meaning Unit Power Instant output Watts (W) Energy Power over time kWh Solar panels are rated in watts, but electricity bills are based on kilowatt-hours. How Much Energy Can Solar Panels Power in a Home? Here’s what 1 solar panel (2 kWh/day) can roughly run: LED lights for an entire day TV for 20–24 hours Ceiling fan for 15–18 hours Laptop for several days Now imagine 15–20 panels working together-that’s enough to power most household needs. Why Actual Solar Energy May Be Lower Than Expected Real-life losses happen due to: Dust and dirt on panels Inverter efficiency losses High temperatures Wiring and system losses That’s why solar installers usually design systems with a buffer so you still meet your energy needs. Is Solar Energy Worth It? Yes, because: You generate your own electricity You reduce dependency on the grid You save on electricity bills Solar panels last
How Does a Solar Farm Work? And Their Benefits

Solar farms are becoming one of the most important sources of clean energy across the world, especially solar farms in India, where sunlight is available for most of the year. As electricity demand rises and fossil fuel costs increase, large-scale solar power projects are helping countries move toward a more sustainable and reliable energy future. What Is a Solar Farm? A solar farm is a large area of land covered with solar panels that generate electricity from sunlight and supply it to homes, businesses, or directly to the power grid. Unlike rooftop solar systems that serve a single building, solar farms produce electricity on a much larger scale. Solar farms are usually built on open land, unused fields, or desert areas where sunlight is available for long hours. These projects are often developed by energy companies or government-supported renewable energy programs. In simple terms: Solar panels capture sunlight Sunlight is converted into electricity Electricity is sent to the grid Homes and industries use this clean power How Does a Solar Farm Work? Understanding how a solar farm works is easier when we break it down step by step. Step 1: Sunlight Hits the Solar Panels Solar panels are made of photovoltaic (PV) cells, usually made from silicon. When sunlight falls on these cells, it knocks electrons loose and creates direct current (DC) electricity. This process is called the photovoltaic effect, and it is the basic working principle of all solar energy systems. Step 2: DC Electricity Is Collected All solar panels in the solar farm are connected through cables. The DC electricity generated by each panel is collected and sent toward central power units. Because solar farms have thousands of panels, proper wiring and layout are extremely important to reduce power loss. Step 3: Inverters Convert DC to AC Power Most homes and industries use alternating current (AC) electricity. So, the DC power generated by solar panels is passed through inverters, which convert DC into AC electricity. Large solar farms usually use: Central inverters String inverters (depending on design and capacity) Step 4: Voltage Is Increased Using Transformers After conversion, the electricity voltage is increased using transformers. This helps transmit power efficiently over long distances without major losses. Step 5: Power Is Supplied to the Grid Finally, the electricity is fed into the local or national power grid. From here, it reaches homes, offices, factories, and other users-just like electricity from any traditional power plant. Main Components of a Solar Farm A solar farm may look simple from outside, but it consists of several important components working together. Solar Panels Capture sunlight and generate DC electricity Installed on fixed structures or tracking systems Mounting Structures Hold solar panels at the correct angle Can be fixed-tilt or solar trackers Inverters Convert DC electricity into usable AC power Ensure grid-compatible output Transformers Increase voltage for long-distance transmission Cables and Junction Boxes Transfer electricity safely and efficiently Monitoring System Tracks energy generation, faults, and efficiency Helps in maintenance and performance optimization Types of Solar Farms Solar farms can be classified based on size, technology, and usage. Utility-Scale Solar Farms Large projects (5 MW to 1000+ MW) Supply electricity directly to the grid Common for government and private power producers Community Solar Farms Smaller solar farms shared by multiple users Ideal for people without rooftop access Floating Solar Farms Built on water bodies like reservoirs and lakes Reduce land use and water evaporation Growing fast in India Solar Farms with Tracking Systems Panels follow the sun’s movement Higher power generation Slightly higher installation cost Solar Farms in India: Current Scenario India is one of the fastest-growing solar energy markets in the world. Due to high solar radiation and strong government support, solar farms in India are expanding rapidly. Key facts: India ranks among the top countries in installed solar capacity States like Rajasthan, Gujarat, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu lead in solar farm projects Government initiatives like the National Solar Mission support large-scale solar farms Solar parks such as Bhadla Solar Park (Rajasthan) are globally recognized Solar farms play a crucial role in reducing India’s dependency on coal and imported fuels. Benefits of Solar Farms Solar farms offer multiple advantages-not just for the environment, but also for the economy and energy security. 1. Clean and Renewable Energy Solar energy comes from the sun, which is unlimited and pollution-free. Solar farms do not release harmful gases or smoke during electricity generation. 2. Lower Electricity Costs in the Long Run Once installed, solar farms have very low operating and maintenance costs. Over time, they help reduce electricity prices and protect against fuel price fluctuations. 3. Energy Security Solar farms reduce dependence on fossil fuels and imported energy sources. This improves national energy security, especially in countries like India. 4. Employment Generation Large solar farm projects create jobs in: Manufacturing Installation Operations and maintenance Engineering and project management 5. Productive Use of Wasteland Many solar farms are built on unused or low-fertility land, turning unproductive areas into energy-generating assets. Challenges Faced by Solar Farms While solar farms have many benefits, they also face some challenges. Land Requirement Solar farms need large areas of land, which can sometimes cause land acquisition issues. Weather Dependency Power generation depends on sunlight, which may vary due to clouds, rain, or dust. Initial Investment The upfront cost of setting up solar farms is high, although costs are decreasing every year. Grid Integration Managing large amounts of solar power requires grid upgrades and energy storage solutions. Environmental Impact of Solar Farms Compared to traditional power plants, solar farms have minimal environmental impact. Positive impacts: Zero air pollution during operation Reduced carbon emissions Lower water usage than thermal power plants Concerns: Land use impact if not planned properly Panel disposal and recycling at end of life With proper planning and recycling policies, solar farms remain one of the most eco-friendly energy options. Solar Farm vs Other Power Sources (Simple Comparison Table) Factor Solar Farms Coal Power Plants Diesel Generators Fuel Cost Free (Sunlight) High
Solar Calculators: A Complete Guide

Solar calculators are simple online tools that help you understand how much solar power you need, how much it may cost, and how much you can save on electricity bills. A solar calculator or solar panel calculator uses basic details like your location, electricity usage, and rooftop area to give you a clear solar estimate in just a few minutes. Renewable energy is no longer the future-it is the present. In India, rising electricity tariffs, frequent power cuts, and strong government support have made solar energy a smart and practical choice for homes and businesses. Still, many people feel confused about costs, system size, and savings. This is exactly where a solar calculator becomes useful. Introduction India is moving fast toward clean energy. The Government of India is actively promoting rooftop solar through schemes like PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana, net metering policies, and state-level subsidies. Solar power not only reduces your electricity bill but also lowers your dependence on fossil fuels. However, switching to solar is a financial decision. Before investing, most people want answers to questions like: How many solar panels do I need? How much will a solar system cost? How much money can I save every month? Is solar worth it for my home or business? A solar energy calculator answers all these questions quickly and transparently. What Is a Solar Calculator? A solar calculator, also known as a solar panel calculator, solar panel cost calculator, solar PV calculator, or solar rooftop calculator, is an online tool designed to estimate your solar requirements. It helps you calculate: Required solar system size (in kW) Approximate installation cost Expected electricity generation Monthly and annual savings Return on investment (ROI) Payback period Most solar calculators work for residential, commercial, and industrial users and are easy enough for anyone to use-even without technical knowledge. Why Solar Calculators Are Important Before Going Solar From real project experience, one common mistake people make is either oversizing or undersizing their solar system. Both lead to problems: Oversizing increases unnecessary costs Undersizing limits savings and efficiency A solar panel calculator prevents these issues by giving data-backed estimates based on your actual usage. Key reasons solar calculators are important: They provide clarity before investment They help in financial planning They reduce dependency on sales guesses They allow fair comparison between vendors How Does a Solar Calculator Work? A solar calculator works in a logical, step-by-step manner. Here’s how most tools function: 1. Collects User Inputs You enter basic details such as: Location (city/state or pin code) Monthly electricity consumption (kWh from your bill) Sanctioned load Rooftop area available 2. Analyzes Solar Potential The calculator uses location-based solar radiation data and average sunlight hours to understand how much energy your panels can generate. 3. Calculates System Size Based on your energy usage, it suggests: Recommended solar capacity (kW) Number of panels required 4. Estimates Cost and Savings It calculates: Approximate installation cost Monthly bill reduction Annual savings 5. Calculates ROI and Payback The solar calculator shows: Payback period (usually 4–6 years) Long-term savings over 25 years Many calculators also factor in government subsidies, making the estimates more realistic. Key Inputs Required for a Solar Panel Calculator To get accurate results, you need a few basic details: Electricity Bill: Monthly or yearly consumption in kWh Location: State and city Rooftop Area: Available shadow-free space Sanctioned Load: Mentioned on your bill Tip from experience: Always use at least 12 months of electricity data to account for seasonal variations. Understanding Solar System Size (kW) Solar systems are measured in kilowatts (kW). A common confusion is assuming higher kW always means better savings. In reality, the best system size depends on usage. Approximate residential guideline: 1 kW solar system generates 4–5 units per day 1 kW requires around 80–100 sq ft rooftop area A solar calculator automatically balances these factors for you. Electricity Cost: Grid vs Solar (Simple Comparison Table) Below is a simple and user-friendly table showing how solar impacts electricity costs. Parameter Grid-Only Usage With Solar System Monthly Units 600 kWh 100–150 kWh Monthly Bill ₹6,000–₹7,000 ₹1,000–₹2,000 Monthly Savings ₹0 ₹4,000–₹5,000 Annual Savings ₹0 ₹48,000–₹60,000 Carbon Emissions High Very Low Electricity Dependency 100% Grid Partial Grid Values are indicative and may vary by location and usage. Benefits of Using a Solar Calculator Using a solar panel calculator offers several practical advantages: 1. Saves Money Planning You know upfront how much you may invest and save, reducing financial uncertainty. 2. Helps Choose the Right System Size No guesswork—only data-based recommendations. 3. Shows Environmental Impact Solar calculators often display CO₂ reduction, helping users understand environmental benefits. 4. ROI Visibility You clearly see when your investment breaks even. 5. Roof Space Assessment It checks whether your rooftop is sufficient for solar installation. 6. Long-Term Financial Planning Calculates savings considering rising electricity prices. Applications of Solar Calculators for Different Users 1. For Businesses Businesses use solar calculators to: Estimate operational cost reduction Understand ROI and depreciation benefits Plan CAPEX or OPEX solar models Many MSMEs can save significant amounts over a system’s lifetime by switching to solar. 2. For Homeowners Homeowners benefit by: Estimating monthly bill reduction Planning system size based on family usage Understanding subsidy impact 3. For Solar Installers Installers use solar calculators to: Generate quick and transparent proposals Build trust with clients Reduce estimation errors 4. For Environmental Groups Solar calculators help: Educate communities Show real data on carbon reduction Promote clean energy adoption How to Calculate Solar Panel Capacity Using a Solar Calculator To calculate solar panel capacity, the solar calculator mainly focuses on two factors: Daily energy consumption Peak sun hours in your region What You Need: Past electricity bills Location details Panel wattage (300W–400W common) The calculator converts this data into required kW capacity automatically. How to Estimate the Number of Solar Panels Needed A solar panel calculator estimates panels using this approach: Step 1: Daily Energy Usage Monthly units ÷ 30 = Daily kWh Step 2: Required System Size Daily kWh ÷ Peak
What Is a Solar Carport? The Ultimate Guide

A solar carport is a smart structure that turns your parking space into a clean energy source. Instead of a normal shed or parking shade, it uses solar panels on the roof to generate electricity while protecting vehicles from sun and rain. In solar carport India, these systems are becoming popular for homes, offices, factories, malls, and public spaces because they solve two problems at once-parking and power generation. In simple words, a solar carport means “park your car and produce electricity at the same time.” What Is a Solar Carport? A solar carport is a covered parking structure with solar panels installed on top. These panels capture sunlight and convert it into electricity that can be used for homes, businesses, or even EV charging. Unlike rooftop solar, a solar carport does not sit on your building. It stands independently over parking areas like: Home driveways Office parking lots Factory parking spaces Hospitals, malls, schools Airports and public parking areas This is why commercial solar carports are especially popular in India-large parking areas are easily converted into power-generating assets. Why Solar Carports Are Growing Fast in India The solar carport India market is growing because of a few strong reasons: Rooftop space is limited in cities Parking areas are unused during most of the day Electricity costs are rising EV adoption is increasing Businesses want visible green solutions From personal experience working on solar projects, many companies realize that their parking area is often bigger than their roof-and it gets full sunlight all day. A solar carport makes perfect sense in such cases. How Does a Solar Carport Work? A solar carport works just like any solar power system, with one key difference-the panels are installed on a parking structure instead of a roof. Working Process Explained Simply Sunlight falls on solar panels installed on the carport roof Solar panels generate DC electricity Inverter converts DC to AC power Electricity is used in your building, EV chargers, or sent to the grid Excess power (if any) can be exported through net metering Because carports are open structures, installers can set the best tilt angle and direction, which often gives better performance than rooftop solar. Key Components of a Solar Carport System A complete solar carport includes: Solar panels (mono or bifacial) Carport structure (steel or aluminum) Mounting system (rails, clamps, fasteners) Inverter AC & DC wiring Earthing and lightning protection Optional EV chargers Optional battery storage Each component affects performance, safety, and long-term durability. Solar Carport Benefits The solar carport benefits go beyond electricity savings. Below are real, practical advantages seen in Indian projects. 1. Lower Electricity Bills Solar carports generate power on-site, reducing dependency on grid electricity. Many commercial users see 30–60% reduction in electricity bills. 2. Best Use of Idle Space Parking areas usually do nothing except hold vehicles. A solar carport converts them into revenue-saving assets without using extra land. 3. Vehicle Protection Cars stay protected from: Harsh sunlight UV damage Rain and dust Bird droppings This improves vehicle life and comfort. 4. Ideal for EV Charging Solar carports are perfect for EV charging stations, especially in offices, malls, and apartments. 5. Higher Solar Capacity Rooftops have limits. Parking areas don’t. This makes commercial solar carports suitable for large systems. 6. Better Panel Orientation Unlike rooftops, carports allow: Ideal tilt angle Zero shading Better airflow (cooler panels = more power) 7. Sustainability & Branding For businesses, solar carports visibly show commitment to green energy. This improves: Brand image ESG score Customer trust 8. Increased Property Value Solar infrastructure adds long-term value to commercial and residential properties. Pros and Cons of Solar Carports (Quick Comparison) Pros Cons Reduces electricity bills Higher upfront cost Uses unused parking space Strong foundation required Protects vehicles Installation takes longer Supports EV charging Needs proper permissions Better solar efficiency Higher structural cost Scalable system Engineering expertise needed Types of Solar Carports in India 1. Residential Solar Carports These are designed for homes with 1–3 vehicles. Best for: Independent houses Villas Farmhouses Capacity: 1 kW – 10 kW Focus: Power savings + car protection Also Read : Residential Solar 2. Commercial Solar Carports These are large installations for businesses and institutions. Best for: Offices Factories Hospitals Malls Airports Capacity: 50 kW to multi-MW Focus: Cost reduction + sustainability goals 3. Public & Institutional Solar Carports Used in: Government buildings Universities Transport hubs These projects often aim at carbon reduction + public awareness. Commercial vs Residential Solar Carport: Key Differences Factor Residential Commercial Size 1–3 cars 20–500+ cars Capacity 1–10 kW 50 kW – 1 MW+ Cost per watt Higher Lower Structure Simple Heavy-duty Installation time 1–3 days Weeks ROI Medium Faster EV integration Optional Common Solar Carport Structure Design: What Matters Most Good structure design is critical for safety and performance. 1. Structural Strength Deep concrete foundation Wind resistance (important in coastal areas) Load-bearing capacity for panels 2. Tilt Angle & Direction Ideal tilt in India: 15–30 degrees Orientation planned for maximum sunlight 3. Water Drainage Proper slope Gutters for rainwater Prevents leakage and corrosion 4. Electrical Safety Proper earthing Lightning protection Protected cable routing 5. Vehicle Clearance Enough height for SUVs Easy movement and parking Step-by-Step Solar Carport Installation Process Site inspection & sunlight analysis Structure design & approvals Foundation construction Structure erection Solar panel installation Electrical wiring & inverter setup Testing & grid connection Monitoring system activation How Much Does a Solar Carport Cost in India? The solar carport cost in India depends on size, design, and location. Estimated Cost Table (India) Category Residential Solar Carport Commercial Solar Carport Typical Size 1–10 kW 50 kW – 1 MW+ Cost per kW (before subsidy) ₹1.1–2 lakh ₹40,000–60,000 Subsidy Up to 40% Not applicable Structure cost ₹6,000–12,000/kW ₹6,000–12,000/kW Payback period 5–7 years 3–5 years Disclaimer Prices mentioned above are basic standard estimates. Actual solar carport prices may vary based on location, structure design, material quality, installation complexity, and market conditions. Applications of Solar Carports in India Residential Use Home power generation EV charging
Solar Panel Maintenance Guide to Improve Efficiency & Lifespan

Solar Panel Maintenance is the key to getting more power and better savings from the same solar setup on your roof. With regular care and simple checks, your solar panels can stay efficient, produce more electricity, and last their full lifespan of 25–30 years without major issues. Many people think solar panels are “install and forget” systems. In reality, even the best solar panels need basic maintenance to perform at their best. Dust, heat, rain, birds, and time slowly affect performance. The good news? Maintaining solar panels is simple, affordable, and highly rewarding in the long run. Why Solar Panel Maintenance Is So Important When you invest in solar energy, you’re making a long-term decision. Solar panels are designed to work for decades, but only if they are looked after properly. Here’s why solar panel maintenance really matters: It keeps solar panel efficiency high It helps you generate maximum electricity It reduces unexpected repair costs It protects your warranty It increases the overall lifespan of the system Studies and real-world performance data show that poorly maintained solar panels can lose 10–20% efficiency over time. On the other hand, well-maintained systems often perform close to their original capacity even after 10–15 years. Simply put: Clean panels = more sunlight = more power = more savings How Solar Panel Maintenance Boosts Efficiency and Lifespan Solar panels work by absorbing sunlight. Anything that blocks sunlight reduces power generation. Over time, the following issues slowly build up: Dust and pollution (very common in Indian cities) Bird droppings Leaves and debris Hard water stains Minor wear and tear Without solar panel maintenance, these small problems add up. Benefits of Regular Solar Panel Maintenance Up to 15% higher energy output Early detection of faults Better return on investment (ROI) Longer system life (25–30 years) Stable inverter and battery performance Regular maintenance doesn’t mean frequent expensive servicing. Most tasks are simple visual checks and basic cleaning. Do Solar Panels Really Need Maintenance? Yes, they do — but not in a complicated way. Solar panels have no moving parts, which makes them low-maintenance compared to other electrical systems. However, “low maintenance” does not mean “no maintenance.” Think of solar panels like a water tank on your roof. It works fine on its own, but if you never clean it, performance drops. Solar panel maintenance ensures: Panels absorb maximum sunlight Electrical connections stay safe Inverters function correctly Long-term efficiency remains stable What Affects Solar Panel Efficiency and Performance? Understanding what impacts solar panel efficiency helps you maintain them better. 1. Dust, Dirt, and Pollution Dust is the biggest enemy of solar panels, especially in India. Even a thin layer of dust can reduce output noticeably. 2. Temperature Solar panels don’t like extreme heat. Efficiency drops by around 1% for every degree above 25°C High heat speeds up material degradation 3. Shading Shadows from: Trees Nearby buildings Antennas or water tanks Even partial shading can affect the entire system. 4. Weather Conditions Heavy rain can cause debris buildup Hail can damage glass Snow (in some regions) blocks sunlight Strong winds loosen fittings 5. Wiring and Inverter Health Loose connections or inverter issues can reduce system output even if panels look clean. Do’s of Solar Panel Maintenance Following these simple habits can keep your system running smoothly for years. Clean Solar Panels Regularly Clean once every 3–6 months More often in dusty or coastal areas Use Gentle Cleaning Methods Soft cloth, sponge, or microfiber mop Normal or soft water Early morning or evening cleaning Inspect Panels Visually Check every few months for: Cracks Discoloration Loose wires Bird nests Monitor Energy Output Use: Mobile apps Online dashboards Monthly electricity bills Sudden drops often signal maintenance needs. Schedule Professional Maintenance Once or twice a year Especially for large or rooftop systems Don’ts of Solar Panel Maintenance Avoid these mistakes to protect your panels and warranty. a. Don’t Use Harsh Chemicals Chemicals can damage: Anti-reflective coating Glass surface b. Don’t Use Hard Brushes or Pressure Washers They can: Scratch panels Cause micro-cracks c. Don’t Walk on Panels This can: Crack cells Void warranties d. Don’t Ignore the Inverter Inverters are the heart of the system. Ignoring them affects overall performance. e. Don’t Attempt Electrical Repairs Always contact certified technicians. Solar Panel Maintenance and Cleaning Guide (Step-by-Step) Solar panel maintenance doesn’t require special tools. Here’s a simple process: Step 1: Safety First Turn off the system if advised Avoid wet or slippery roofs Step 2: Gentle Cleaning Use water and a soft sponge Remove dust, bird droppings, and stains No detergents unless approved Step 3: Dry the Panels Let them air-dry naturally Avoid leaving water spots Step 4: Visual Inspection Look for: Cracks Burn marks Loose wiring Step 5: Monitor Output Check daily or weekly energy generation. Simple Solar Panel Maintenance Checklist Maintenance Task Frequency Panel cleaning Every 3–6 months Visual inspection Monthly Inverter check Monthly Output monitoring Weekly Professional servicing Once a year Wiring inspection Yearly This table makes solar panel maintenance easy and user-friendly for homeowners. How to Monitor Solar Panel Health and Efficiency Most modern systems come with monitoring tools that show: Daily energy generation Monthly trends Performance alerts Signs You Need Solar Panel Maintenance Sudden drop in power output Inverter warning lights Higher electricity bills Uneven panel performance Monitoring helps catch problems early before they turn expensive. How Extreme Weather Impacts Solar Panels Solar panels are built tough, but nature can still affect them. High Heat Reduces efficiency Speeds up aging Heavy Rain and Storms Causes debris buildup Can loosen fittings Hail May crack glass in extreme cases Snow and Ice Blocks sunlight Usually slides off tilted panels Regular solar panel maintenance after extreme weather is strongly recommended. How Often Do Solar Panels Need Maintenance? General guideline: Cleaning: 2–4 times a year Inspection: Once a year Monitoring: Ongoing In high-dust areas: Cleaning may be needed every 15–30 days Solar panel maintenance frequency depends on: Location Weather Pollution levels Solar Panel Maintenance Cost in India Solar panel maintenance is affordable compared
7 New Solar Panel Technology Trends for 2026 in India

Solar panel technology is evolving faster than ever, and India is right at the center of this transformation. In just a few years, solar has moved from being an “alternative” energy source to a mainstream power solution for homes, businesses, factories, and even cities. By 2026, new innovations will make solar systems more efficient, flexible, smarter, and easier to integrate into everyday life. At KLK Ventures, we closely track how solar panel technology is changing on the ground-from manufacturing trends to real installation challenges in Indian conditions like heat, dust, space limitations, and grid reliability. This guide is written to genuinely help homeowners, EPC contractors, builders, and business owners understand what’s coming next, without hype or technical jargon. Why Solar Panel Technology Matters More Than Ever in India India’s solar journey is not just about clean energy – it’s about affordability, energy independence, and reliability. Some key realities driving innovation: High electricity demand and frequent peak load issues Rising power tariffs for commercial and industrial users Limited rooftop space in urban areas Extreme weather conditions (heat, dust, humidity) Government targets of 500 GW renewable capacity by 2030 To solve these challenges, solar panel technology must deliver: Higher efficiency in less space Better performance in Indian climates Lower long-term cost per unit Smarter systems with storage and monitoring Now let’s explore the 7 most important solar panel technology trends for 2026 in India. 1. High-Efficiency Solar Panels Crossing 25% What’s Changing Traditional solar panels used to convert only about 10–15% of sunlight into electricity. Today, thanks to advanced cell designs like TOPCon, HJT, and n-type cells, efficiencies are crossing 22–25%, and this trend will strengthen by 2026. Why It Matters in India More power from small rooftops Lower balance-of-system costs (less wiring, fewer structures) Ideal for apartments, factories, and urban homes Practical Insight In cities like Delhi, Mumbai, and Bengaluru, rooftop space is limited. High-efficiency solar panel technology allows the same roof to generate 20–30% more electricity without expanding area. Real-World Benefit Smaller system size Faster ROI Better performance in low-light and winter conditions 2. Perovskite Solar Cells: The Biggest Breakthrough What Are Perovskite Solar Cells? Perovskites are advanced semiconductor materials that absorb light more efficiently than traditional silicon. They can be manufactured at lower temperatures and costs. Why This Solar Panel Technology Is a Game-Changer Lower manufacturing cost Higher efficiency potential Lightweight and flexible designs Tandem Technology Explained (Simple Words) Perovskite cells are layered on top of silicon cells: Silicon captures long wavelengths Perovskite captures short wavelengths Together, they generate more power from the same sunlight. Current Progress Global lab efficiencies above 26% Pilot manufacturing already started Commercial availability expected to expand by 2026 Indian Impact This technology can: Reduce solar panel prices in the long term Enable solar on weak roofs and mobile structures Increase adoption in rural and semi-urban areas 3. Bifacial Solar Panels Becoming the New Standard What Are Bifacial Solar Panels? Unlike traditional panels, bifacial panels generate electricity from both sides – front and back. How They Work Front side absorbs direct sunlight Back side captures reflected light from ground, tiles, concrete, or sand Why India Is Perfect for Bifacial Technology High solar radiation Concrete rooftops and reflective surfaces Large solar parks and open installations Key Benefits 5–15% extra energy generation Better performance in open and elevated installations Longer lifespan due to glass-glass design Common Applications Utility-scale solar plants Commercial rooftops Carports and ground-mounted systems 4. Flexible & Lightweight Solar Panel Technology What’s New New materials allow solar panels to be: Thin Bendable Extremely lightweight Where Traditional Panels Fail Weak rooftops Temporary structures Curved surfaces New Use Cases in India Warehouses with metal sheet roofs Portable solar for agriculture Solar on vehicles, sheds, and remote sites Practical Advantage These panels can be: Rolled and transported easily Installed without heavy mounting structures Used where glass panels are unsafe Future Outlook By 2026, flexible solar panel technology will grow rapidly in: Defense Disaster relief Rural electrification Smart mobility 5. Solar Panels Integrated with Energy Storage Why Storage Is No Longer Optional Solar generates power during the day, but demand continues at night. That’s where energy storage comes in. What’s Improving Lithium-ion battery efficiency Longer battery life cycles Smarter battery management systems (BMS) Benefits of Solar + Storage Backup during power cuts Reduced grid dependency Peak load management for industries Indian Context With frequent outages and voltage fluctuations, solar panel technology combined with storage is becoming essential for: Hospitals Data centers Manufacturing units Smart homes 6. Transparent Solar Panels for Buildings What Are Transparent Solar Panels? These panels look like glass but generate electricity by capturing invisible light (UV and infrared). Where They Are Used Office windows Building facades Skylights Commercial complexes Why This Matters for Urban India Limited rooftop space High-rise buildings with large glass areas Growing demand for green buildings Key Advantage Buildings can generate power without changing their appearance. Future Scope By 2026, transparent solar panel technology will support: Net-zero buildings Smart cities Green architecture projects 7. Smart Solar Panels with AI & IoT What Makes Solar “Smart”? Smart solar panel technology uses: Sensors AI-based monitoring IoT connectivity What It Can Do Track performance in real time Detect faults early Optimize energy output automatically Why It’s Useful in India Reduces maintenance costs Prevents unnoticed power loss Improves system lifespan Simple Comparison Table: Solar Panel Technology Trends (2026) Technology Type Key Benefit Best Use Case High-Efficiency Panels More power in less space Urban rooftops Perovskite Cells Low cost + high efficiency Future mass adoption Bifacial Panels Extra energy from reflection Solar farms, carports Flexible Panels Lightweight & bendable Weak roofs, mobile use Solar + Storage Power anytime Homes, industries Transparent Panels Energy + design Smart buildings Smart Solar Panels Performance optimization All system sizes Cost Expectations (Basic & Standard Estimate) Disclaimer: The prices mentioned below are basic standard estimates only. Actual prices may vary depending on brand, location, installation type, subsidies, raw material costs, and market conditions. Solar Panel Technology Approx. Price Range (₹/Watt) Standard Mono
Solar-Powered EV Charging Stations Cost and Benefits

Solar-Powered EV Charging is emerging as a practical and future-ready solution as electric vehicles become more common across India. A solar-powered EV charging station uses energy from the sun to charge electric vehicles, reducing electricity costs, lowering carbon emissions, and supporting sustainable transport. With rising fuel prices and increasing pressure on the power grid, a solar powered charging station offers a cleaner and more cost-effective alternative for homes, businesses, and public charging networks. Growing Need for Solar-Powered EV Charging Stations in India India is seeing rapid growth in both solar energy and electric vehicles. As of June 2024, India’s installed solar energy capacity has reached 85.47 GW, and it continues to grow every year. At the same time, EV adoption is accelerating due to government incentives, rising petrol and diesel prices, and increasing environmental awareness. The challenge now is charging infrastructure. If EVs are charged only through conventional grid electricity-much of which still comes from coal-the environmental benefit reduces. This is where solar-powered EV charging stations play an important role. India receives an average of 300 sunny days per year, making it one of the best countries in the world to use solar energy efficiently. Combining solar PV systems with EV charging helps maximize this natural advantage. What Is a Solar-Powered EV Charging Station? A solar-powered EV charging station is a setup where solar photovoltaic (PV) panels generate electricity that is used to charge electric vehicles. The system may be: Grid-connected (solar + grid backup) Off-grid (solar + battery storage) Hybrid (solar + battery + grid) Key Components Involved Solar PV panels Inverter (converts DC to AC) EV charger (AC or DC) Battery storage (optional but useful) Energy monitoring system During the day, solar panels produce electricity that directly powers the EV charger. Any excess energy can be stored in batteries or exported to the grid, depending on the system design. How Solar-Powered EV Charging Works (Simple Explanation) Sunlight falls on solar panels Panels generate DC electricity Inverter converts DC to usable AC power EV charger supplies electricity to the vehicle Extra power is stored or sent to the grid This process runs automatically and requires minimal manual intervention once installed. Cost of Setting Up a Solar-Powered EV Charging Station The cost of a solar-powered EV charging station depends on several factors such as charger type, solar capacity, battery requirement, and installation location. Major Cost Components Solar panels EV charging equipment Inverter and electrical hardware Civil and installation work Battery storage (if required) Approximate Cost Breakdown (Indicative) Component Estimated Cost Range Solar panels (5–10 kW) ₹2.5 – ₹5 lakh Level 2 AC charger ₹50,000 – ₹1,00,000 DC fast charger ₹5 – ₹15 lakh Inverter & wiring ₹1 – ₹2 lakh Battery storage (optional) ₹2 – ₹6 lakh Installation & civil work ₹1 – ₹2 lakh Note: These are basic standard prices for general understanding. Actual costs may vary depending on brand, location, site conditions, and system size. Per-Unit Electricity Cost: Solar vs Grid Power One of the biggest advantages of solar-powered EV charging is lower electricity cost over the long term. Cost Comparison Source Approximate Cost per kWh Solar power ₹2.5 – ₹3 Grid (commercial) ₹6 – ₹8 Grid (residential) ₹4 – ₹7 Solar energy becomes significantly cheaper once the initial investment is recovered, especially for commercial EV charging stations with high daily usage. Economic Benefits of Solar-Powered EV Charging Stations 1. Lower Charging Cost for EV Owners Charging with solar power reduces the cost per kilometer for EV users. This makes electric vehicles even more economical compared to petrol or diesel vehicles. 2. Protection from Rising Electricity Tariffs Grid electricity prices tend to increase over time. Solar power provides price stability, helping businesses and homeowners manage long-term costs. 3. Reduced Operational Expenses Once installed, solar-powered EV charging stations have low running and maintenance costs. Solar panels typically last 25-30 years. 4. Attractive Return on Investment (ROI) For high-usage locations like offices, malls, fleets, and highways, solar-powered EV charging stations can achieve ROI in 4-6 years, depending on usage and subsidies. Impact on Overall Cost of EV Ownership Using solar power for EV charging significantly reduces lifetime vehicle costs: Lower fuel expenses Less dependence on external power sources Stable charging cost over years Increased savings over vehicle lifespan This improves EV adoption, especially among cost-conscious buyers. Government Subsidies and Financial Incentives India strongly supports renewable energy and EV infrastructure through multiple schemes. Available Benefits Include Capital subsidies on solar installations Incentives under FAME scheme for EV infrastructure Accelerated depreciation for businesses State-level solar and EV policies Low-interest green loans These incentives can reduce initial investment significantly, making solar-powered EV charging stations more affordable. Environmental Benefits of Solar-Powered EV Charging Stations Reduction in Carbon Emissions Solar-powered EV charging stations produce zero emissions during operation. This directly reduces CO₂ emissions from transportation. Lower Dependence on Fossil Fuels Charging EVs with solar energy reduces coal and oil usage, helping India move toward energy independence. Improved Air Quality Reduced fossil fuel use leads to lower air pollution, especially in cities with heavy traffic. Long-Term Sustainability Solar energy is renewable and abundant, making it a reliable long-term solution. Deployment Benefits in Remote and Rural Areas Works Where Grid Power Is Weak or Unavailable Solar-powered EV charging stations can operate independently, making them ideal for rural highways, villages, and remote locations. Easy to Scale Stations can be expanded by adding more panels or chargers as demand increases. Cost-Effective Infrastructure Avoids expensive grid extension and reduces transmission losses. Support for Rural EV Adoption Affordable charging options Job creation in installation and maintenance Better mobility and connectivity Reduced dependence on diesel transport Challenges of Solar-Powered EV Charging Stations High Initial Investment Upfront costs for solar panels, chargers, and batteries can be high without subsidies. Space Requirement Solar installations need adequate rooftop or open land space. Battery Cost Energy storage systems increase project cost but improve reliability. Lack of Standardization Different EV charging standards can create compatibility issues. Current Market Scenario and Future Outlook India has attracted $3.8
