Solar Energy for Agriculture
- Home
- Blogs
Farming in India is rapidly evolving. With increasing fuel prices and unreliable energy sources, more farmers are adopting solar energy systems. Clean, renewable, and inexpensive — and especially powerful in rural areas — it provides an alternative to diesel fuel and electric energy.
Solar energy for agriculture isn’t just about going green — it’s about saving money, improving yields, and achieving self-sufficiency. It provides farmers with more productivity using fewer inputs, from irrigation to cold storage. Let’s look at the transition to solar energy in Indian agriculture.
Why Solar Energy is Perfect for Indian Farmers
India has over 300 sunny days a year. This makes it the ideal country to use solar energy on farms. Instead of depending on diesel pumps or grid electricity, farmers can use sunlight to power essential tools and systems.
Key benefits:
Works in off-grid rural areas
Lowers electricity and fuel costs
Reduces carbon emissions
Makes farming more sustainable
Supports government subsidy schemes
By using solar energy, farmers can control costs and increase productivity without harming the environment.
How Solar Energy is Used in Agriculture
Solar energy is now used in many smart ways on Indian farms — from running water pumps to lighting storage sheds. These solutions help reduce fuel dependency and boost overall efficiency. Learn more about its practical applications in solar power for agriculture.
There are many ways solar power helps farmers in their day-to-day work:
There are many ways solar power helps farmers in their day-to-day work:
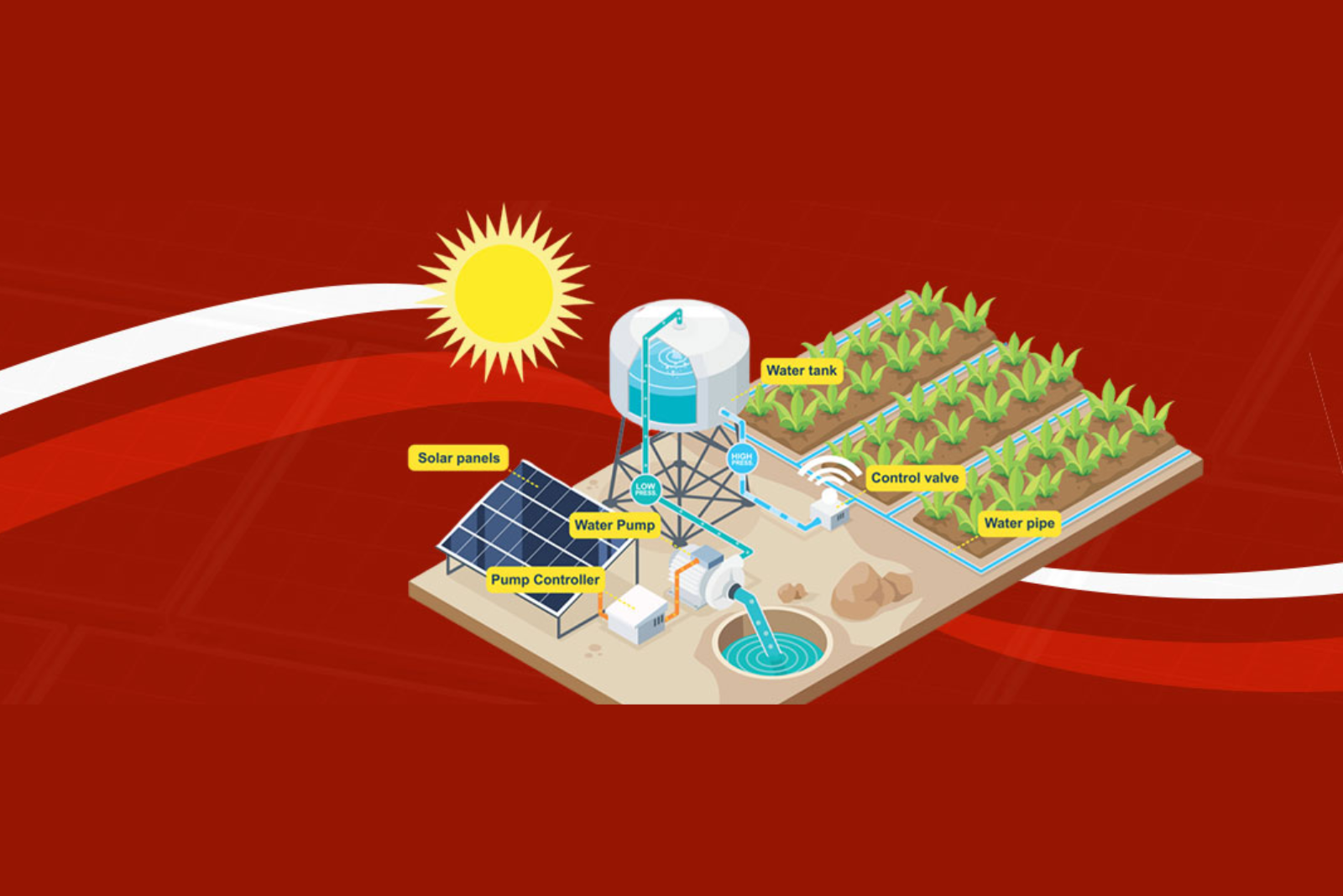
1. Solar Water Pumps
One of the most popular uses is for irrigation. Diesel pumps are expensive to run. Grid power is unreliable. But solar water pumps solve both problems.
Benefits:
Works anywhere with sunlight
No fuel costs
Low maintenance
Long lifespan (15–20 years)
To understand how these pumps work and their types, visit our detailed guide on what is a solar water pump and different types of solar water pumps.
2. Solar Fencing
Solar-powered fencing keeps crops safe from animals without needing grid power.
Advantages:
Prevents animal entry
Charges automatically during the day
Works well in forest-border areas
Saves cost over electric fencing
This is ideal for regions with wildlife or night-time crop raids.
3. Solar Dryers
Post-harvest losses can be high due to improper drying. Solar dryers help farmers dry grains, fruits, and vegetables quickly and hygienically.
Why use them:
Faster than sun drying
Protects from insects and rain
Increases product quality and shelf life
Solar dryers help small farmers earn more from their harvest.
4. Solar-Powered Cold Storage
Perishable crops like fruits and milk need cooling. In rural areas, solar cold storage helps preserve produce longer.
Features:
Runs fully on solar power
Keeps temperature stable
Reduces spoilage and waste
Improves bargaining power for farmers
Many FPOs and co-operatives are now setting up solar-powered storage units in villages.
5. Solar Lighting for Farms
Lighting is needed for night work, animal care, and safety. Solar street lights and lanterns are a simple solution.
Use cases:
Cattle sheds
Poultry farms
Field boundaries
Farmhouses
How Much Can Farmers Save with Solar?
Installing a solar pump may seem costly at first, but the savings over the years are significant. The cost of installing a solar water pump system in India depends on multiple factors like HP rating, panel type, and installation region. Thanks to subsidies and financing, it’s now more affordable than ever.
Why it’s worth it:
Zero fuel costs after installation
No monthly electricity bills
Less maintenance over the long run
Pays for itself in a few years through savings
With proper upkeep, a solar system can last well over a decade.
Government Schemes That Support Solar for Agriculture
India’s PM-KUSUM scheme and other subsidies are making solar systems more accessible for farmers. From eligibility to applying for a subsidy, you can explore the complete process in our blog on Solar KUSUM C Yojana benefits, eligibility, and application process.
The Indian government supports solar adoption in farming through various programs.
Key schemes:
PM-KUSUM (Kisan Urja Suraksha evam Utthaan Mahabhiyan)
Farmers get up to 30% support on solar pumps
Encourages off-grid solar solutions
Extra power can be sold back to the electricity board
State-level schemes offering extra benefits in states like Maharashtra, Gujarat, and Rajasthan
NABARD-supported loans for easier financing
Net metering for earning credit on unused electricity
These initiatives are making solar a long-term, low-risk investment for the agricultural sector.
Challenges in Using Solar for Farming
Challenge | Solution |
High initial cost | Use government subsidy and flexible bank finance |
Dust on panels | Use solar cleaning systems to maintain output |
Lack of awareness | Set up demo farms and local training sessions |
Technical breakdown | Partner with experienced AMC service providers for routine checks |
Choosing the Right Solar System for Your Farm
Before buying, farmers should check:
Daily electricity or water needs
Type of pump required (surface/submersible)
Availability of rooftop or ground space
Access to subsidies and support programs
Warranty and post-sale services
Future of Solar Energy in Agriculture
The future of farming will depend on clean and smart energy systems.
Upcoming trends:
Solar-powered tractors and threshers
Drip irrigation linked with solar sensors
Community-based solar grids in rural areas
AI tools that automate irrigation based on sunlight
More awareness through government outreach and training
Final Thoughts
Solar energy in agriculture is no longer a “good idea” – it is becoming absolutely necessary for the future of farming in India. Solar energy provides a way for farmers to reduce their costs, boost production, and reduce their reliance on erratic grid power or expensive diesel.
With increasing government backing, improvements in technology, and increasing awareness of the use of solar energy, it is a matter of time before solar-farming become mainstream. Whether it be a small lighting solution or an entire solar irrigation system, investing today could provide for a greener and more profitable tomorrow.
